Create and track plots from experiments
6 minute read
wandb.plot의 메소드를 사용하면 트레이닝 중 시간에 따라 변하는 차트를 포함하여 wandb.log로 차트를 추적할 수 있습니다. 사용자 정의 차트 프레임워크에 대해 자세히 알아보려면 이 가이드를 확인하십시오.
기본 차트
이러한 간단한 차트를 사용하면 메트릭 및 결과의 기본 시각화를 쉽게 구성할 수 있습니다.
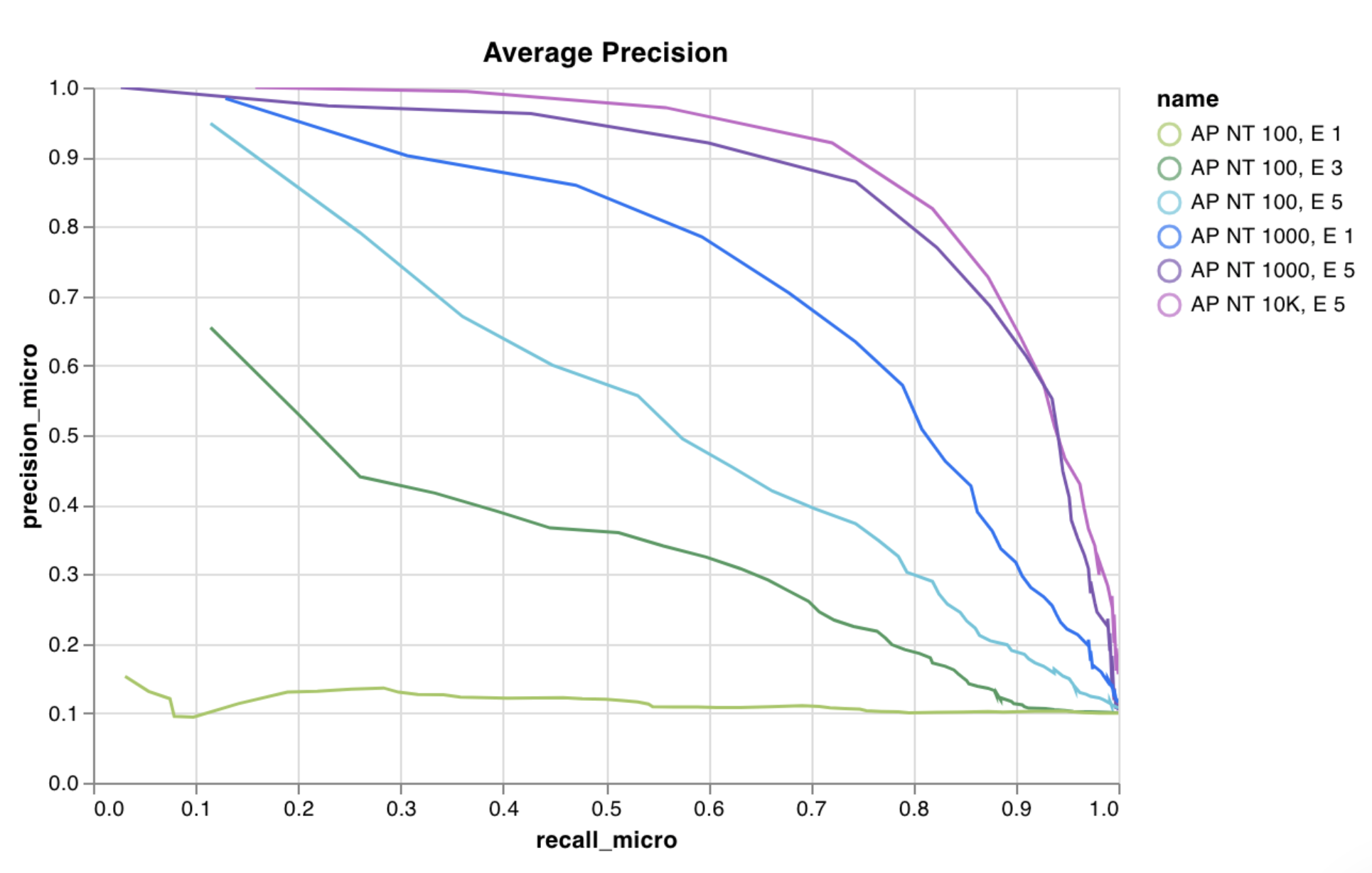
wandb.plot.line()
임의의 축에서 연결되고 정렬된 점 목록인 사용자 정의 라인 플롯을 기록합니다.
data = [[x, y] for (x, y) in zip(x_values, y_values)]
table = wandb.Table(data=data, columns=["x", "y"])
wandb.log(
{
"my_custom_plot_id": wandb.plot.line(
table, "x", "y", title="Custom Y vs X Line Plot"
)
}
)
이를 사용하여 임의의 두 차원에 대한 곡선을 기록할 수 있습니다. 두 값 목록을 서로 플로팅하는 경우 목록의 값 수는 정확히 일치해야 합니다. 예를 들어 각 점에는 x와 y가 있어야 합니다.
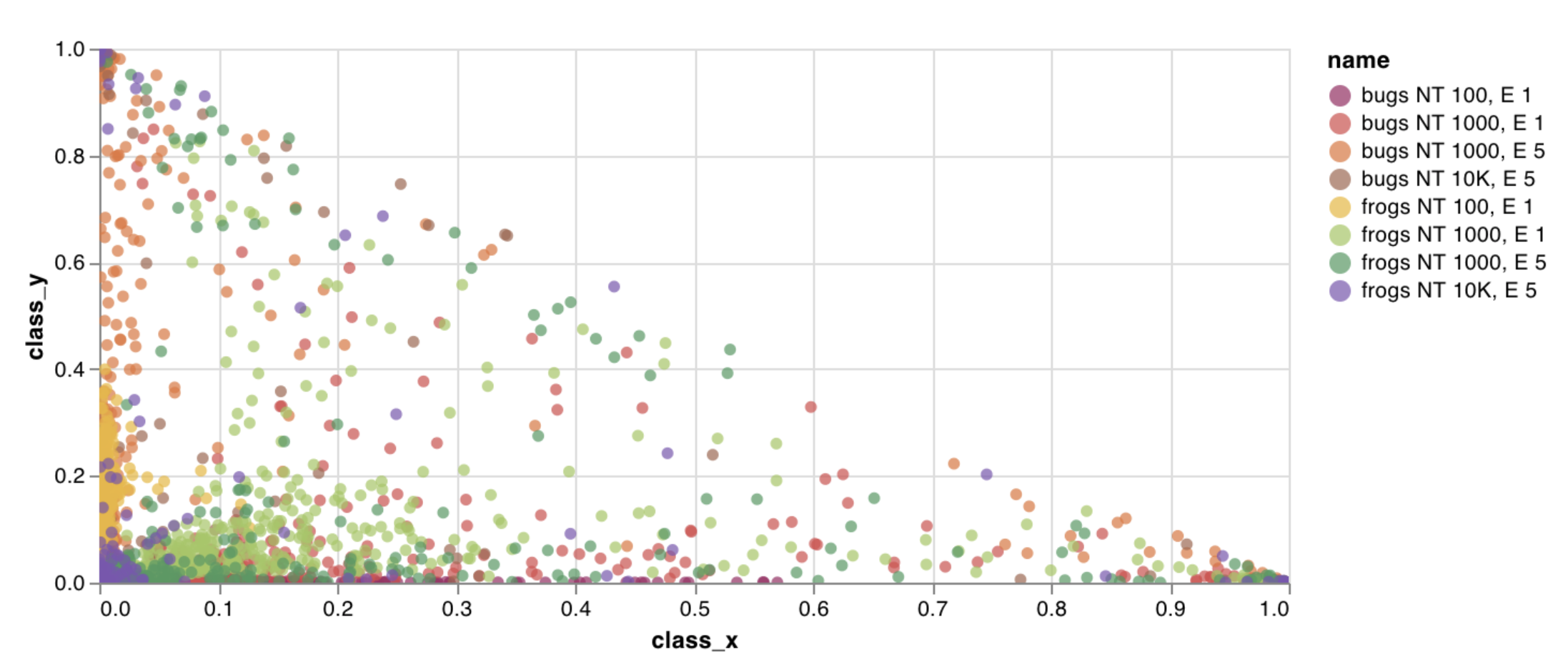
wandb.plot.scatter()
임의의 축 x 및 y 쌍에 대한 점 (x, y) 목록인 사용자 정의 스캐터 플롯을 기록합니다.
data = [[x, y] for (x, y) in zip(class_x_scores, class_y_scores)]
table = wandb.Table(data=data, columns=["class_x", "class_y"])
wandb.log({"my_custom_id": wandb.plot.scatter(table, "class_x", "class_y")})
이를 사용하여 임의의 두 차원에 대한 스캐터 점을 기록할 수 있습니다. 두 값 목록을 서로 플로팅하는 경우 목록의 값 수는 정확히 일치해야 합니다. 예를 들어 각 점에는 x와 y가 있어야 합니다.
wandb.plot.bar()
몇 줄의 코드로 레이블이 지정된 값 목록을 막대로 표시하는 사용자 정의 막대 차트를 기본적으로 기록합니다.
data = [[label, val] for (label, val) in zip(labels, values)]
table = wandb.Table(data=data, columns=["label", "value"])
wandb.log(
{
"my_bar_chart_id": wandb.plot.bar(
table, "label", "value", title="Custom Bar Chart"
)
}
)
이를 사용하여 임의의 막대 차트를 기록할 수 있습니다. 목록의 레이블과 값 수는 정확히 일치해야 합니다. 각 데이터 포인트에는 레이블과 값이 모두 있어야 합니다.
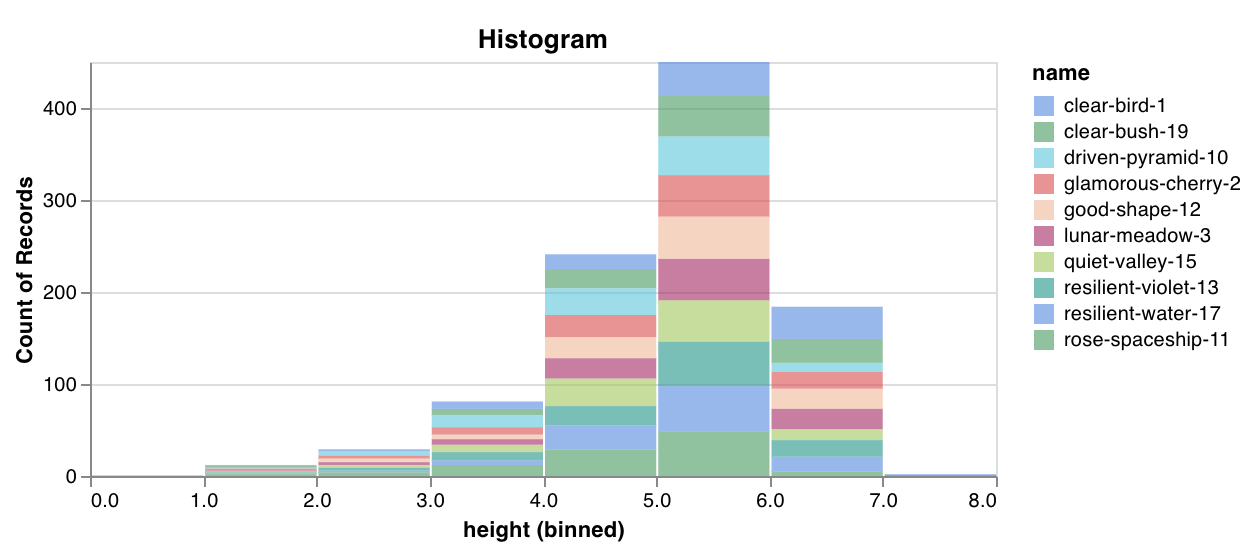
wandb.plot.histogram()
몇 줄의 코드로 값 목록을 발생 횟수/빈도별로 bin으로 정렬하는 사용자 정의 히스토그램을 기본적으로 기록합니다. 예측 신뢰도 점수 목록 (scores)이 있고 분포를 시각화하고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다.
data = [[s] for s in scores]
table = wandb.Table(data=data, columns=["scores"])
wandb.log({"my_histogram": wandb.plot.histogram(table, "scores", title="Histogram")})
이를 사용하여 임의의 히스토그램을 기록할 수 있습니다. data는 행과 열의 2D 배열을 지원하기 위한 목록의 목록입니다.
wandb.plot.line_series()
하나의 공유된 x-y 축 집합에 여러 라인 또는 여러 x-y 좌표 쌍 목록을 플로팅합니다.
wandb.log(
{
"my_custom_id": wandb.plot.line_series(
xs=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
ys=[[10, 20, 30, 40, 50], [0.5, 11, 72, 3, 41]],
keys=["metric Y", "metric Z"],
title="Two Random Metrics",
xname="x units",
)
}
)
x 및 y 점의 수는 정확히 일치해야 합니다. y 값의 여러 목록과 일치시키기 위해 x 값 목록 하나를 제공하거나 y 값의 각 목록에 대해 별도의 x 값 목록을 제공할 수 있습니다.
모델 평가 차트
이러한 사전 설정 차트에는 스크립트에서 직접 차트를 빠르게 쉽게 기록하고 UI에서 찾고 있는 정확한 정보를 볼 수 있도록 하는 기본 제공 wandb.plot 메소드가 있습니다.
wandb.plot.pr_curve()
한 줄로 Precision-Recall curve를 만듭니다.
wandb.log({"pr": wandb.plot.pr_curve(ground_truth, predictions)})
코드가 다음에 엑세스할 수 있을 때마다 이를 기록할 수 있습니다.
- 예제 집합에 대한 모델의 예측 점수 (
predictions) - 해당 예제에 대한 해당 그라운드 트루스 레이블 (
ground_truth) - (선택 사항) 레이블/클래스 이름 목록 (
labels=["cat", "dog", "bird"...]레이블 인덱스 0이 cat, 1 = dog, 2 = bird 등을 의미하는 경우) - (선택 사항) 플롯에서 시각화할 레이블의 서브셋 (여전히 목록 형식)
wandb.plot.roc_curve()
한 줄로 ROC curve를 만듭니다.
wandb.log({"roc": wandb.plot.roc_curve(ground_truth, predictions)})
코드가 다음에 엑세스할 수 있을 때마다 이를 기록할 수 있습니다.
- 예제 집합에 대한 모델의 예측 점수 (
predictions) - 해당 예제에 대한 해당 그라운드 트루스 레이블 (
ground_truth) - (선택 사항) 레이블/클래스 이름 목록 (
labels=["cat", "dog", "bird"...]레이블 인덱스 0이 cat, 1 = dog, 2 = bird 등을 의미하는 경우) - (선택 사항) 플롯에서 시각화할 이러한 레이블의 서브셋 (여전히 목록 형식)
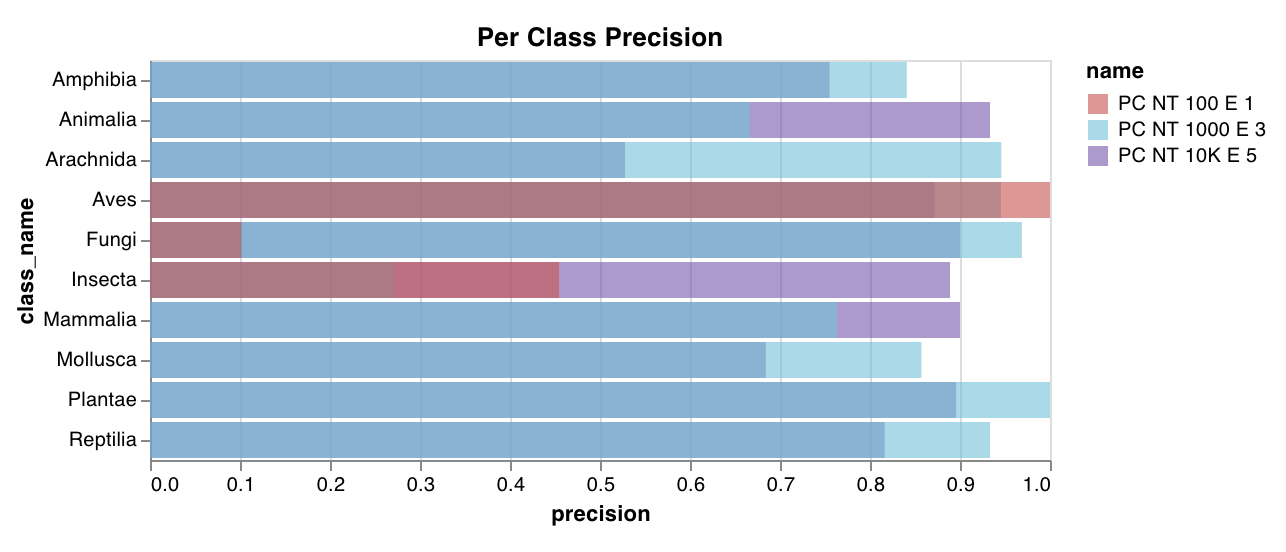
wandb.plot.confusion_matrix()
한 줄로 다중 클래스 confusion matrix를 만듭니다.
cm = wandb.plot.confusion_matrix(
y_true=ground_truth, preds=predictions, class_names=class_names
)
wandb.log({"conf_mat": cm})
코드가 다음에 엑세스할 수 있을 때마다 이를 기록할 수 있습니다.
- 예제 집합에 대한 모델의 예측 레이블 (
preds) 또는 정규화된 확률 점수 (probs). 확률은 (예제 수, 클래스 수) 모양이어야 합니다. 확률 또는 예측값 중 하나를 제공할 수 있지만 둘 다 제공할 수는 없습니다. - 해당 예제에 대한 해당 그라운드 트루스 레이블 (
y_true) class_names문자열로 된 레이블/클래스 이름의 전체 목록. 예:class_names=["cat", "dog", "bird"]인덱스 0이cat, 1이dog, 2가bird인 경우
인터랙티브 사용자 정의 차트
전체 사용자 정의를 위해 기본 제공 사용자 정의 차트 사전 설정을 조정하거나 새 사전 설정을 만든 다음 차트를 저장합니다. 차트 ID를 사용하여 스크립트에서 직접 해당 사용자 정의 사전 설정에 데이터를 기록합니다.
# 플로팅할 열이 있는 테이블을 만듭니다.
table = wandb.Table(data=data, columns=["step", "height"])
# 테이블의 열에서 차트의 필드로 매핑합니다.
fields = {"x": "step", "value": "height"}
# 테이블을 사용하여 새 사용자 정의 차트 사전 설정을 채웁니다.
# 자신의 저장된 차트 사전 설정을 사용하려면 vega_spec_name을 변경하십시오.
# 제목을 편집하려면 string_fields를 변경하십시오.
my_custom_chart = wandb.plot_table(
vega_spec_name="carey/new_chart",
data_table=table,
fields=fields,
string_fields={"title": "Height Histogram"},
)
Matplotlib 및 Plotly 플롯
wandb.plot으로 W&B 사용자 정의 차트를 사용하는 대신 matplotlib 및 Plotly로 생성된 차트를 기록할 수 있습니다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4])
plt.ylabel("some interesting numbers")
wandb.log({"chart": plt})
matplotlib 플롯 또는 그림 오브젝트를 wandb.log()에 전달하기만 하면 됩니다. 기본적으로 플롯을 Plotly 플롯으로 변환합니다. 플롯을 이미지로 기록하려면 플롯을 wandb.Image에 전달할 수 있습니다. Plotly 차트도 직접 허용합니다.
fig = plt.figure()로 플롯과 별도로 그림을 저장한 다음 wandb.log 호출에서 fig를 기록할 수 있습니다.W&B Tables에 사용자 정의 HTML 로그
W&B는 Plotly 및 Bokeh의 인터랙티브 차트를 HTML로 기록하고 이를 Tables에 추가하는 것을 지원합니다.
Plotly 그림을 HTML로 Tables에 로그
HTML로 변환하여 인터랙티브 Plotly 차트를 wandb Tables에 기록할 수 있습니다.
import wandb
import plotly.express as px
# 새 run 초기화
run = wandb.init(project="log-plotly-fig-tables", name="plotly_html")
# 테이블 만들기
table = wandb.Table(columns=["plotly_figure"])
# Plotly 그림에 대한 경로 만들기
path_to_plotly_html = "./plotly_figure.html"
# Plotly 그림 예제
fig = px.scatter(x=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4], y=[0, 1, 4, 9, 16])
# Plotly 그림을 HTML에 쓰기
# auto_play를 False로 설정하면 테이블에서 애니메이션 Plotly 차트가 자동으로 재생되지 않습니다.
fig.write_html(path_to_plotly_html, auto_play=False)
# Plotly 그림을 HTML 파일로 테이블에 추가
table.add_data(wandb.Html(path_to_plotly_html))
# 테이블 로그
run.log({"test_table": table})
wandb.finish()
Bokeh 그림을 HTML로 Tables에 로그
HTML로 변환하여 인터랙티브 Bokeh 차트를 wandb Tables에 기록할 수 있습니다.
from scipy.signal import spectrogram
import holoviews as hv
import panel as pn
from scipy.io import wavfile
import numpy as np
from bokeh.resources import INLINE
hv.extension("bokeh", logo=False)
import wandb
def save_audio_with_bokeh_plot_to_html(audio_path, html_file_name):
sr, wav_data = wavfile.read(audio_path)
duration = len(wav_data) / sr
f, t, sxx = spectrogram(wav_data, sr)
spec_gram = hv.Image((t, f, np.log10(sxx)), ["Time (s)", "Frequency (hz)"]).opts(
width=500, height=150, labelled=[]
)
audio = pn.pane.Audio(wav_data, sample_rate=sr, name="Audio", throttle=500)
slider = pn.widgets.FloatSlider(end=duration, visible=False)
line = hv.VLine(0).opts(color="white")
slider.jslink(audio, value="time", bidirectional=True)
slider.jslink(line, value="glyph.location")
combined = pn.Row(audio, spec_gram * line, slider).save(html_file_name)
html_file_name = "audio_with_plot.html"
audio_path = "hello.wav"
save_audio_with_bokeh_plot_to_html(audio_path, html_file_name)
wandb_html = wandb.Html(html_file_name)
run = wandb.init(project="audio_test")
my_table = wandb.Table(columns=["audio_with_plot"], data=[[wandb_html], [wandb_html]])
run.log({"audio_table": my_table})
run.finish()
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.